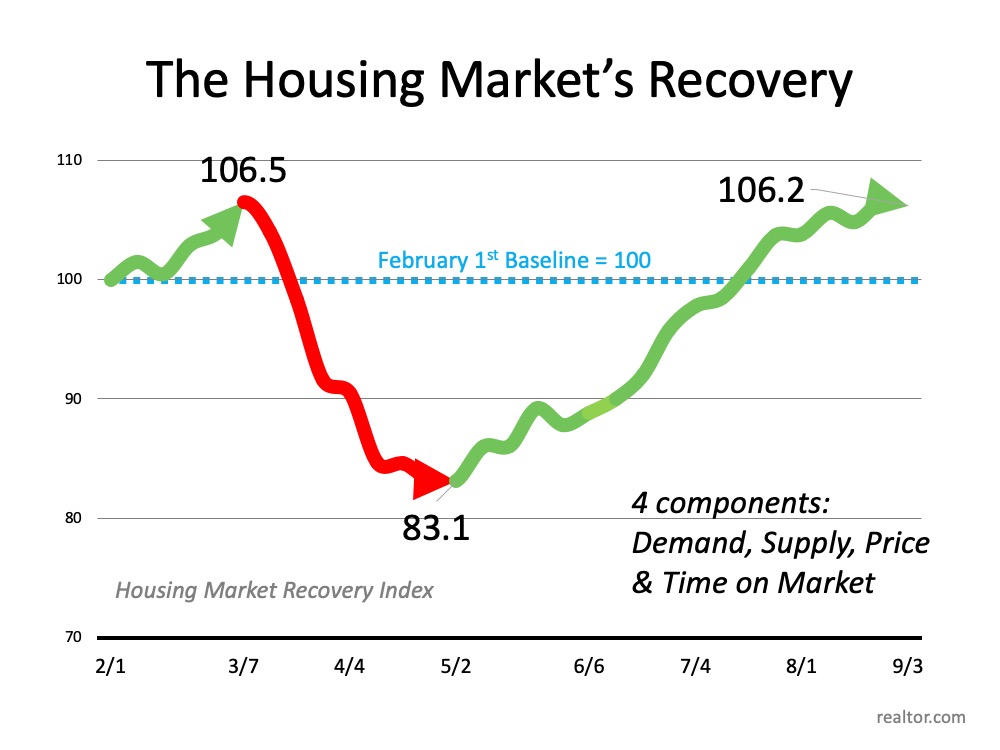
The Latest Unemployment Rate Fell to 8.4%


Last Friday, the Bureau for Labor Statistics released their Employment Report for August 2020. The big surprise was that the unemployment rate fell to 8.4%, a full percent lower than what many analysts had forecasted earlier in the week. Though it is tough to look at this as great news when millions of Americans are still without work, the number of unemployed is currently much lower than most experts had projected it would be just a few months ago.
Not Like the Great Depression or even the Great Recession
Jason Furman, Professor of Practice at Harvard explained:
“An unemployment rate of 8.4% is much lower than most anyone would have thought it a few months ago. It is still a bad recession but not a historically unprecedented event or one we need to go back to the Great Depression for comparison.”
During the Great Depression, the unemployment rate was over 20% for four consecutive years (1932 – 1935). This April, the rate jumped to 14.7%, but has fallen each month since.
During and after the Great Recession (2007-2009), the unemployment rate was at 9% or greater for thirty consecutive months (April 2009 – October 2011). Most economists believe the current rate will continue to fall monthly as the economy regains its strength.
What Happens Going Forward?
The outcome will be determined by how quickly we can contain the virus. In their last Economic Forecasting Survey, the Wall Street Journal reported the economists surveyed believe the annual unemployment rates will be 6.6% in 2021 and 5.5% in 2022. Though that will still be greater than the 3.5% rate that we saw earlier this year, it is lower than the annual rate reported in 2011 (8.5%), 2012 (7.9%), and 2013 (6.7%).
Bottom Line
There are still millions of Americans struggling through this economic downturn. There is, however, a light at the end of the tunnel. The unemployment situation did not get as bad as many had predicted, and the recovery is taking place faster than most thought would happen.
Forbearance Numbers Are Lower than Expected
Originally, some housing industry analysts were concerned that the mortgage forbearance program (which allows families to delay payments to a later date) could lead to an increase in foreclosures when forbearances end. Some even worried that we might relive the 2006-2008 housing crash all over again. Once you examine the data, however, that seems unlikely.
As reported by Odeta Kushi, Deputy Chief Economist for First American:
“Despite the federal foreclosure moratorium, there were fears that up to 30% of homeowners would require forbearance, ultimately leading to a foreclosure tsunami. Forbearance did not hit 30%, but rather peaked at 8.6% and has been steadily falling since.”
According to the most current data from Black Knight, the percentage of homes in forbearance has fallen to 7.4%. The report also gives the decrease in raw numbers:
“The overall trend of incremental improvement in the number of mortgages in active forbearance continues. According to the latest data from Black Knight’s McDash Flash Forbearance Tracker, the number of mortgages in active forbearance fell by another 71,000 over the past week, pushing the total under 4 million for the first time since early May.”
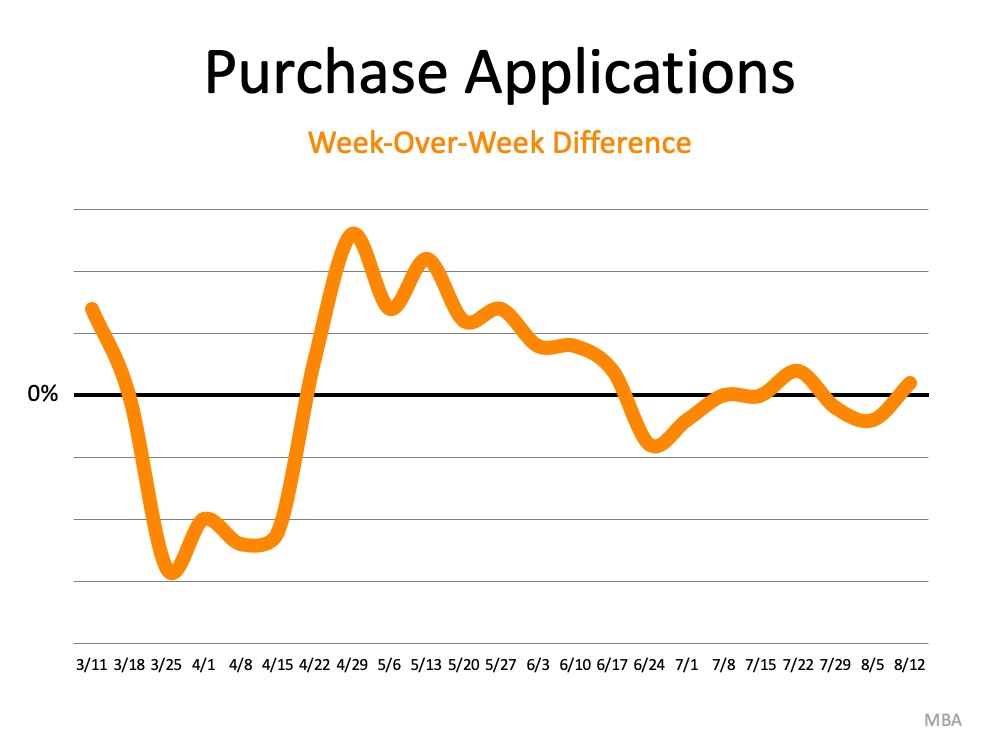
Here’s a graph showing the decline in forbearances over the last several months: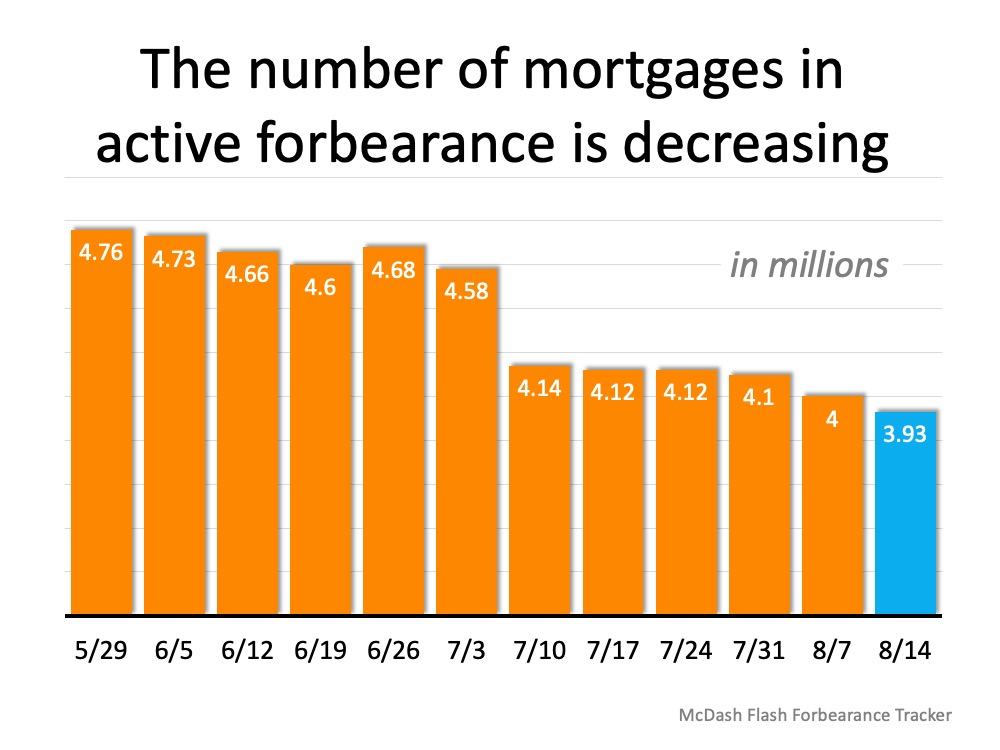 The report also explains that across the board, overall forbearance activity fell with 10% fewer new forbearance requests and nearly 40% fewer renewals.
The report also explains that across the board, overall forbearance activity fell with 10% fewer new forbearance requests and nearly 40% fewer renewals.
What about potential foreclosures once forbearances end?
Kushi also addresses this question:
“There are two main reasons why this crisis is unlikely to produce a wave of foreclosures similar to the 2008 recession. First, the housing market is in a much stronger position compared with a decade ago. Accompanied by more rigorous lending standards, the household debt-to-income ratio is at a four-decade low and household equity near a three-decade high. Indeed, thus far, MBA data indicates that the majority of homeowners who took advantage of forbearance programs are either staying current on their mortgage or paying off the loan through a home sale or a refinance. Second, this service sector-driven recession is disproportionately impacting renters.”
There is one potential challenge
Today, the options available to homeowners will prevent a large spike in foreclosures. That’s good not just for those families impacted, but for the overall housing market. A recent study by Fannie Mae, however, reveals that many Americans are not aware of the options they have.
It’s imperative for potentially impacted families to better understand the mortgage relief programs available to them, for their personal housing situation and for the overall real estate market.
Bottom Line
If Americans fully understand their options and make good choices regarding those options, the current economic slowdown does not need to lead to mass foreclosures.
The Beginning of an Economic Recovery


The news these days seems to have a mix of highs and lows. We may hear that an economic recovery is starting, but we’ve also seen some of the worst economic data in the history of our country. The challenge today is to understand exactly what’s going on and what it means relative to the road ahead. We’ve talked before about what experts expect in the second half of this year, and today that progress largely hinges upon the continued course of the virus.
A recent Wall Street Journal survey of economists noted, “A strong economic recovery depends on effective and sustained containment of Covid-19.” Given the uncertainty around the virus, we can also see what economists are forecasting for GDP in the third quarter of this year (see graph below):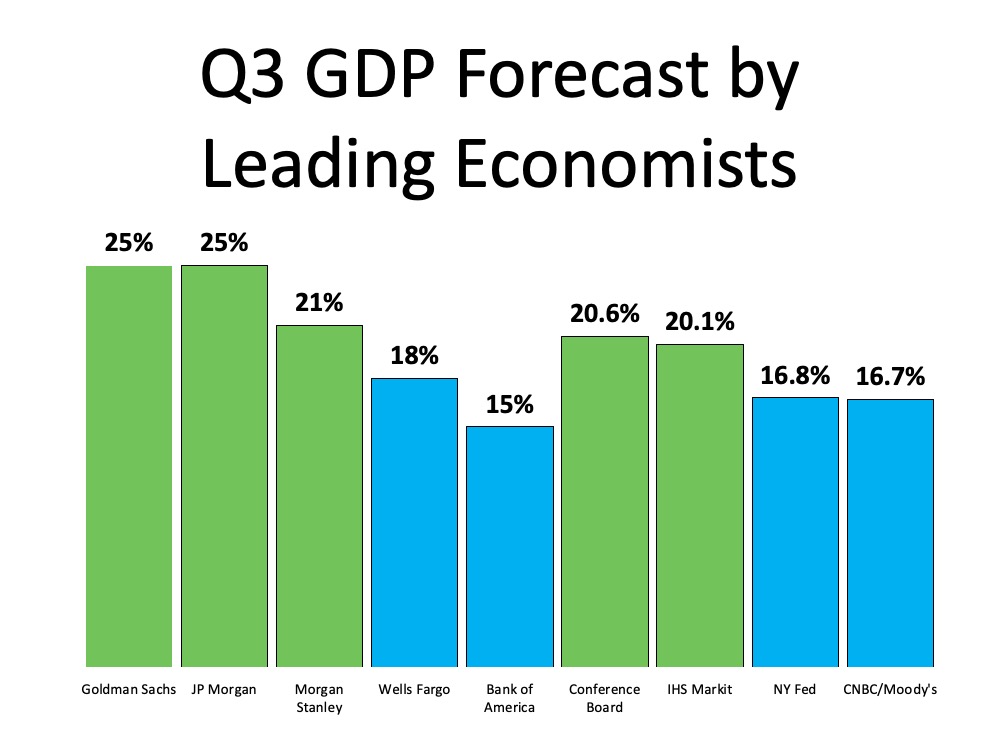 Overwhelmingly, economists are projecting GDP growth in the third quarter of 2020, with 5 of the 9 experts indicating over 20% growth.
Overwhelmingly, economists are projecting GDP growth in the third quarter of 2020, with 5 of the 9 experts indicating over 20% growth.
Lisa Shalett, Chief Investment Officer for Morgan Stanley puts it this way:
“Indeed, the ‘worst ever’ GDP reading could be followed by the ‘best ever’ growth in the third quarter.”
As we look forward, we can expect consumer spending to improve as well. According to Opportunity Insights, as of August 1, consumer spending was down just 7.8% as compared to January 1 of this year.
Bottom Line
An economic recovery is beginning to happen throughout the country. While there are still questions that need to be answered about the road ahead, we can expect to see improvement this quarter.
Why Foreclosures Won’t Crush the Housing Market Next Year


With the strength of the current housing market growing every day and more Americans returning to work, a faster-than-expected recovery in the housing sector is already well underway. Regardless, many are still asking the question: will we see a wave of foreclosures as a result of the current crisis? Thankfully, research shows the number of foreclosures is expected to be much lower than what this country experienced during the last recession. Here’s why.
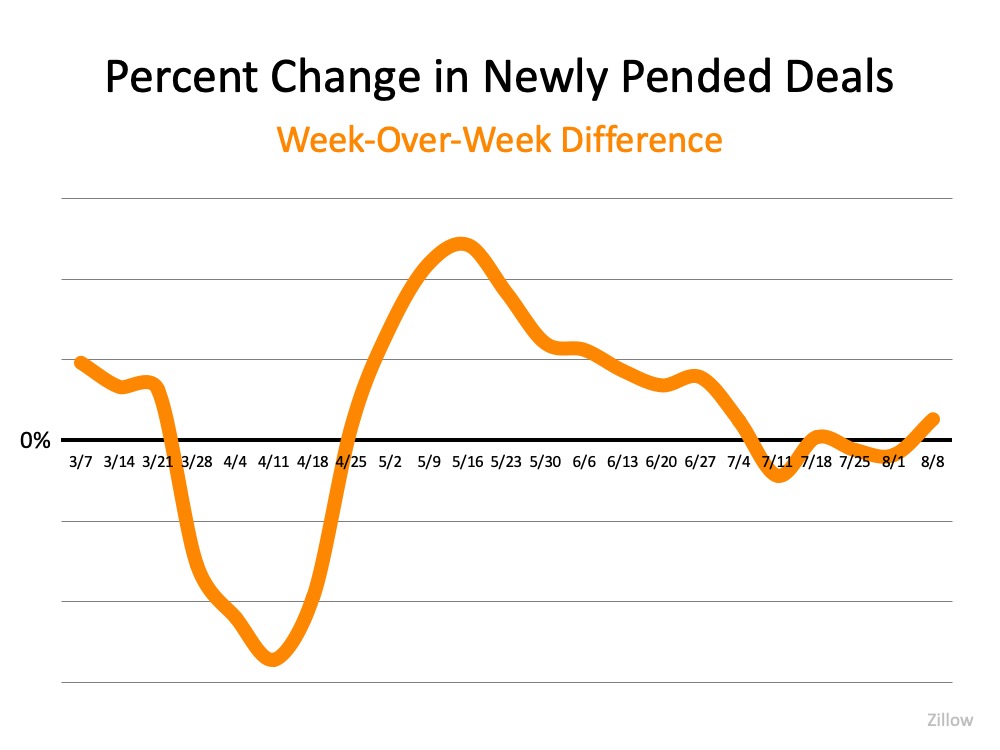
According to Black Knight Inc., the number of those in active forbearance has been leveling-off over the past month (see graph below):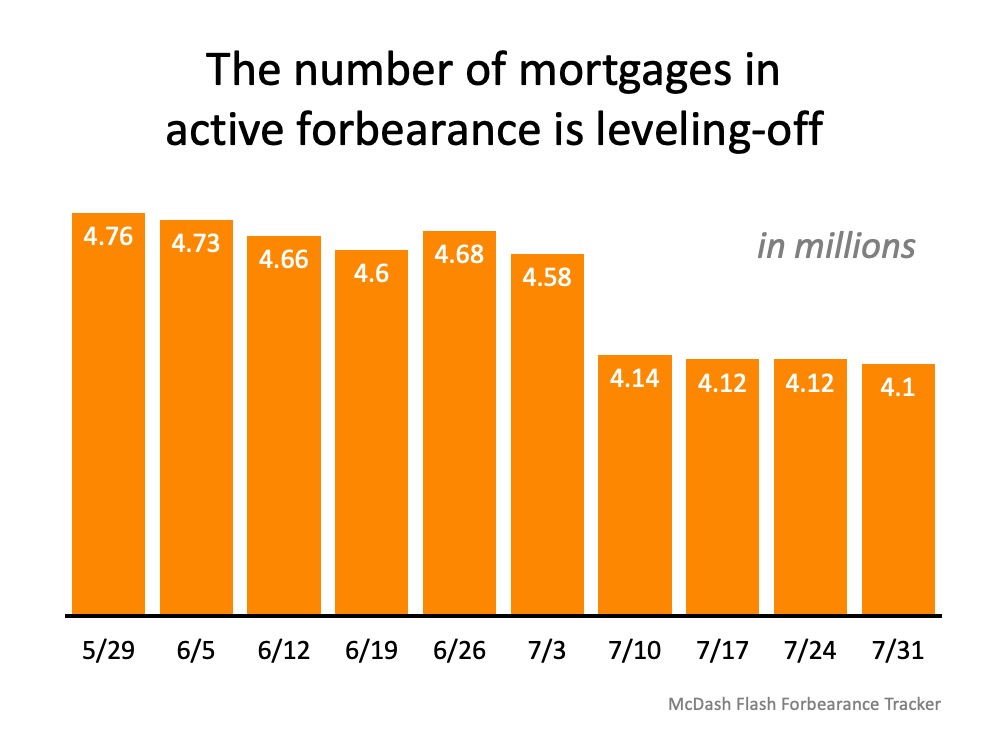 Black Knight Inc. also notes, of the original 4,208,000 families granted forbearance, only 2,588,000 of these homeowners got an extension. Many homeowners have once again started to pay their mortgages, paid off their homes, or never went delinquent on their payments in the first place. They may have applied for forbearance out of precaution, but never fully acted on it (see graph below):
Black Knight Inc. also notes, of the original 4,208,000 families granted forbearance, only 2,588,000 of these homeowners got an extension. Many homeowners have once again started to pay their mortgages, paid off their homes, or never went delinquent on their payments in the first place. They may have applied for forbearance out of precaution, but never fully acted on it (see graph below):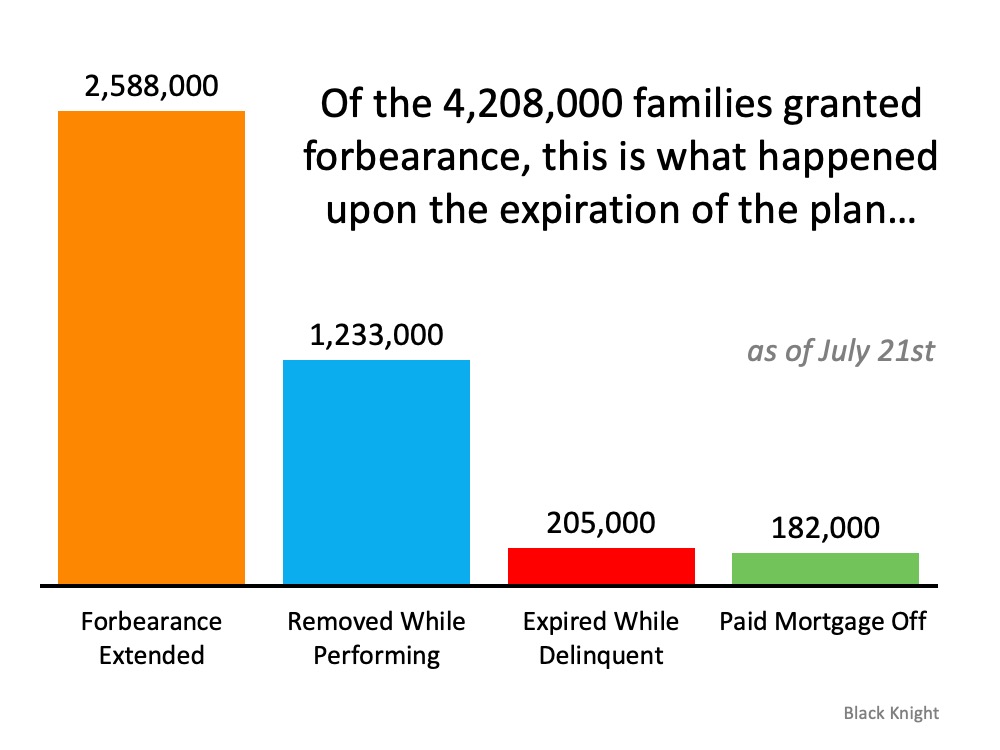 The housing market, and homeowners, therefore, are in a much better position than many may think. Much of that has to do with the fact that today’s homeowners have more equity than most realize. According to John Burns Consulting, over 42% of homes are owned free and clear, meaning they are not tied to a mortgage. Of the remaining 58%, the average homeowner has $177,000 in equity. That number is keeping many homeowners afloat today and giving them options to avoid foreclosure.
The housing market, and homeowners, therefore, are in a much better position than many may think. Much of that has to do with the fact that today’s homeowners have more equity than most realize. According to John Burns Consulting, over 42% of homes are owned free and clear, meaning they are not tied to a mortgage. Of the remaining 58%, the average homeowner has $177,000 in equity. That number is keeping many homeowners afloat today and giving them options to avoid foreclosure.
While ATTOM Data Solutions indicates that there is a potential for the number of foreclosures to increase throughout the country, it’s important to understand why they won’t rock the housing market this time around:
“The United States faces a possible foreclosure surge over the coming months that could more than double the number of households threatened with eviction for not paying their mortgages.”
That number may sound massive, but it is actually much smaller than it seems at first glance. Today’s actual quarterly active foreclosure number is 74,860. That’s over 7.5x lower than the number of foreclosures the country saw at the peak of the housing crash in 2009. When looking at the graph below, it’s clear that even if the number of quarterly foreclosures today doubles, as ATTOM Data Solutions indicates is a possibility (not a given), they will only reach what historically-speaking is a normalized range, far below what up-ended the housing market roughly 10 years ago.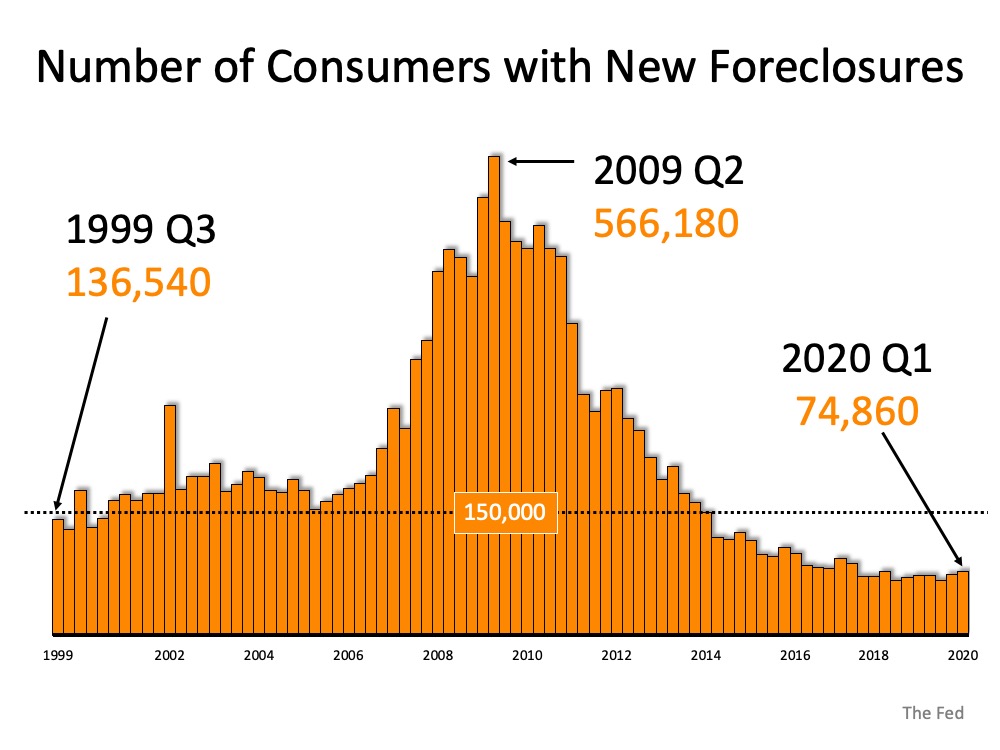 Equity is growing, jobs are returning, and the economy is slowly recovering, so the perfect storm for a wave of foreclosures is not realistically in the housing market forecast. As Odeta Kushi, Deputy Chief Economist for First American notes:
Equity is growing, jobs are returning, and the economy is slowly recovering, so the perfect storm for a wave of foreclosures is not realistically in the housing market forecast. As Odeta Kushi, Deputy Chief Economist for First American notes:
“Alone, economic hardship and a lack of equity are each necessary, but not sufficient to trigger a foreclosure. It is only when both conditions exist that a foreclosure becomes a likely outcome.”
While our hearts are with anyone who may end up in foreclosure as a result of this crisis, we do know that today’s homeowners have more options than they did 10 years ago. For some, it may mean selling their house and downsizing with that equity, which is a far better outcome than a foreclosure.
Bottom Line
Homeowners today have many options to avoid foreclosure, and equity is surely helping to keep many afloat. Even if today’s rate of foreclosures doubles, it will still only hit a mark that is more in line with a historically normalized range, a very good sign for homeowners and the housing market.
The Latest Unemployment Report: Slow and Steady Improvement


Last Friday, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its latest Employment Situation Summary. Going into the release, the expert consensus was for 1.58 million jobs to be added in July, and for the unemployment rate to fall to 10.5%.
When the official report came out, it revealed that 1.8 million jobs were added, and the unemployment rate fell to 10.2% (from 11.1% last month). Once again, this is excellent news as this was the third consecutive month the unemployment rate decreased.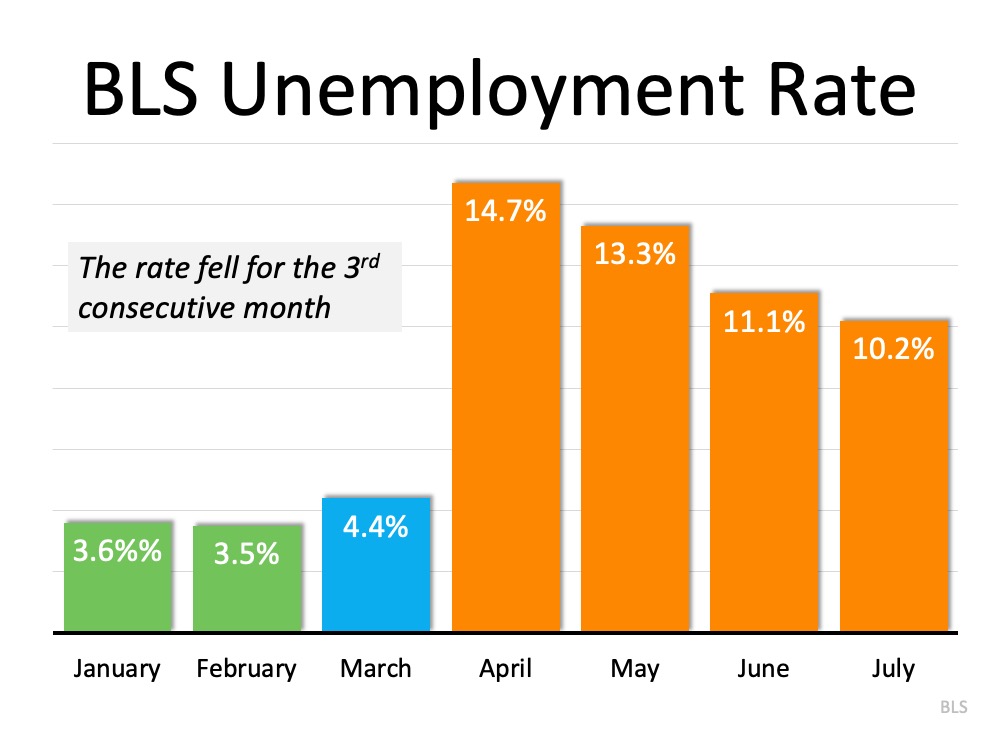 There is, however, still a long way to go before the job market fully recovers. The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) put a potential date on that recovery:
There is, however, still a long way to go before the job market fully recovers. The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) put a potential date on that recovery:
“July’s payroll growth, at 1.8 million, still leaves total payrolls 12.9 million lower than in February. And yet if job gains continued at July’s pace, that deficit will be erased by March 2021. If payrolls reclaim their last peak in 13 months, that would be remarkably fast. It took more than six years after the last recession.”
Permanent vs. Temporary Unemployment
During a pandemic, it’s important to differentiate those who have lost their jobs on a temporary basis from those who have lost them on a permanent basis. Morgan Stanley economists noted in the same WSJ article:
“The rate of churn in the labor market remains incredibly high, but a notable positive detail in this month’s report was the downtick in the rate of new permanent layoffs.”
To address this, the core unemployment rate becomes increasingly important. It identifies the number of people who have permanently lost their jobs. This measure subtracts temporary layoffs and adds unemployed who did not search for a job recently. Jed Kolko, Chief Economist at Indeed and the founder of the index reported:
“Core unemployment fell in July for the first time in the pandemic. That’s the good news I was hoping for.”
What about the housing market?
The housing market has continued to show tremendous resilience during the pandemic. Commenting on the labor report, Robert Dietz, Chief Economist for the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB), tweeted:
“Housing continues to rebound in another positive labor market report. Home builder and remodeler job gains of 24K for July. Residential construction employment down just 56.4K compared to a year ago. Total residential construction employment at 2.85 million.”
Bottom Line
We should remain cautious in our optimism, as the recovery is ultimately tied to our future success in mitigating the ongoing health crisis. However, as Mike Fratantoni, Chief Economist for the Mortgage Bankers Association reminds us: “The pace of job growth slowed in July, but the gains over the past three months represent an impressive rebound during the ongoing economic challenges brought forth by the pandemic.”


 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link